In the fast-paced world of trading, understanding the core movements of the market is crucial for any investor looking to capitalize on fluctuations in price. These movements—Expansion, Retracement, Reversal, and Consolidation—are the foundational elements that paint the broader picture of market trends and opportunities. A trader’s ability to recognize and interpret these movements can make the difference between a savvy investment and a missed opportunity. Each element signifies a different phase of market activity, from the dynamic surges of Expansion to the strategic pauses of Consolidation, providing clues on where the market might head next. For traders looking to harness the rhythm of the market, mastering these four elements is essential.
Here is a table summarizing the key elements of trading: Expansion, Retracement, Reversal, and Consolidation, along with their descriptions, key indicators, and trading strategies:
| Element | Description | Key Indicators | Trading Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion | Significant directional price movement signaling strong market sentiment. | Strong volume, breakout from resistance/support levels. | Join the momentum by trading in the direction of the trend. |
| Retracement | Temporary reversal in trend, offering entry points in the prevailing trend. | Support/resistance levels, Fibonacci retracement, trendlines. | Look for potential end of retracement to enter the trend. |
| Reversal | Fundamental change in market direction, indicating a new trend. | Pattern recognition (e.g., head and shoulders), volume analysis. | Close positions aligned with old trend, initiate new positions for new trend. |
| Consolidation | Period of sideways movement, indicating market indecision before the next move. | Price range-bound, chart patterns like channels or triangles. | Plan for next moves, watch for breakout or breakdown from pattern. |
This table provides a concise overview of these essential market movements, helping traders to better understand and apply these concepts in their trading strategies
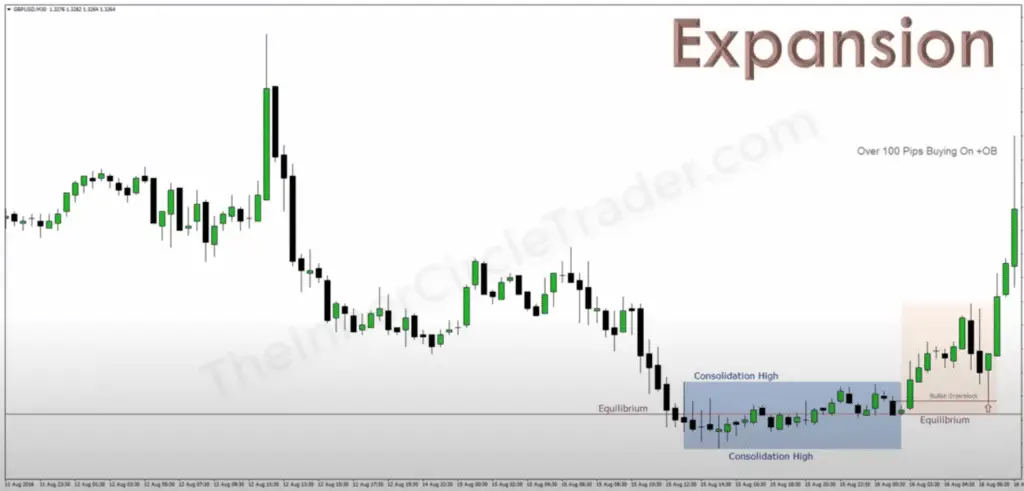
1. Expansion
In trading, Expansion refers to a phase where price moves significantly in one direction, showcasing a strong trend. Imagine a balloon being inflated — this is akin to the market expanding as more traders buy or sell aggressively, pushing prices higher or lower. During Expansion, the market is making its intentions clear; it’s moving with conviction, and this is where trends are born. Traders look for Expansion to join in the momentum, riding the wave of a bullish run for profits or catching a bearish slide to capitalize on declines. Identifying an Expansion phase early can be the key to entering a trade that aligns with the powerful forces of market demand or supply.
2. Retracemet
In the world of trading, a Retracement is a temporary reversal in the prevailing trend of a stock’s price. Think of it like a pit stop in a car race – a brief moment where drivers refuel before speeding off again. In market terms, after a strong price move during Expansion, Retracement is the market taking a breath, with prices pulling back a bit as some traders take profits and others jump in, expecting the trend to continue.
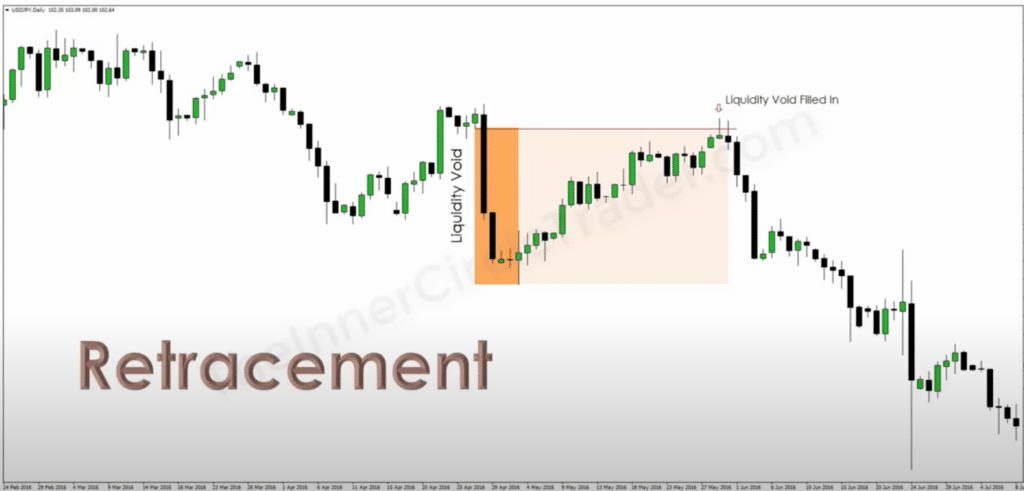
Here’s a structured breakdown of what Retracement involves:
- Nature: Short-term and against the main trend.
- Duration: Varies, but typically not long-lasting.
- Opportunity: Provides entry points for traders who missed the initial trend.
- Identification: Often associated with support and resistance levels.
- Confirmation: Can be identified using technical indicators like Fibonacci retracement levels, moving averages, or trendlines.
- Strategy: Traders may look for signals that the Retracement is ending to enter in the direction of the original trend, expecting the price to resume its prior course.
Traders value Retracements for the entry opportunities they provide, allowing them to join the prevailing trend at better prices. Recognizing a Retracement in the heat of market activity requires a cool head and a keen eye on technical analysis tools.
3. Reversal
In trading, a Reversal signifies a fundamental change in the direction of a stock’s price. Picture a train switching tracks — this is what happens during a Reversal, where the market sentiment shifts, leading prices to move in the opposite direction of the prevailing trend.
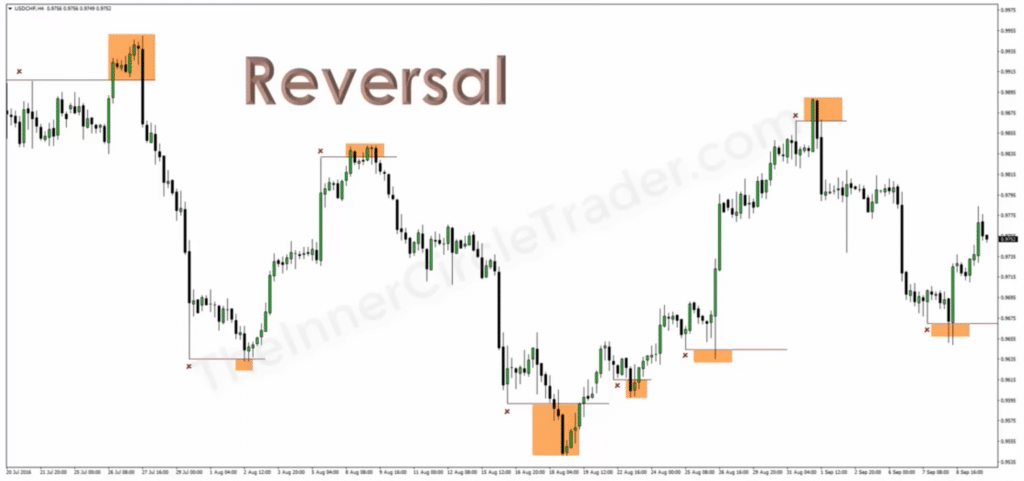
Key aspects of a Reversal include:
- Definition: A Reversal is when the price movement changes course, transitioning from an uptrend to a downtrend, or vice versa.
- Significance: It indicates a significant change in market forces and sentiment, often driven by substantial news or economic events.
- Identification: Traders identify Reversals using patterns like head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and trendline breaks.
- Confirmation: Confirmation through volume analysis and other indicators like moving averages or momentum oscillators is crucial to distinguish Reversals from Retracements.
- Strategy: In a Reversal, traders might close existing positions aligned with the old trend and initiate new positions that align with the new trend direction.
- Risk: Mistaking a Retracement for a Reversal can lead to premature or incorrect trades, highlighting the importance of confirmation.
4. Consolidation
In trading, Consolidation is a period where the price of a stock or asset moves within a confined range, indicating a balance between supply and demand. Imagine a tug of war where neither side gains ground – this is what happens during Consolidation, as the market takes a pause from a definitive trend.
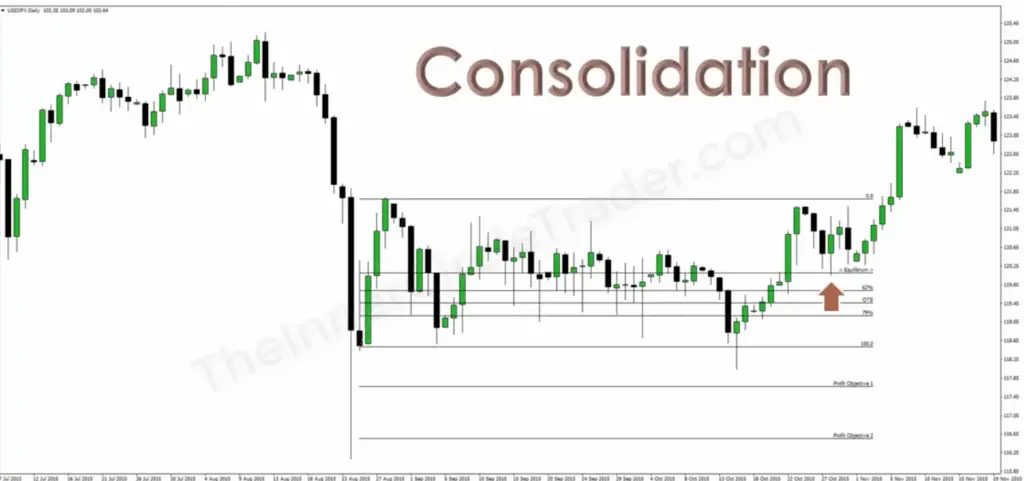
Key aspects of Consolidation include:
- Definition: Consolidation is characterized by prices moving sideways, neither trending upwards nor downwards significantly.
- Characteristics: This phase is marked by a series of higher lows and lower highs, forming a visual pattern that can resemble a rectangle or a triangle on the chart.
- Duration: It can last for a short period or extend over a longer timeframe, depending on market conditions and underlying factors.
- Significance: Consolidation often indicates indecision in the market, as traders are assessing the next major move.
- Identification: It’s identified through chart patterns like channels, wedges, or flags, and can occur after a sharp price movement.
- Strategy: Traders might use this period to plan their next moves, waiting for a breakout or breakdown from the Consolidation pattern as a signal to enter a new position.
- Breakout/Breakdown: A breakout (upwards) or breakdown (downwards) from the Consolidation pattern can signify the start of a new trend.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the concepts of Expansion, Retracement, Reversal, and Consolidation is essential for any trader seeking to navigate the complexities of the financial markets. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in understanding market dynamics and informs strategic decision-making.
- Expansion signals a strong directional move, offering opportunities for traders to ride the momentum.
- Retracement provides a chance to enter an existing trend at a more favorable price point.
- Reversal marks a significant change in market direction, often leading to the formation of new trends.
- Consolidation is a period of market pause, reflecting a balance of forces and setting the stage for the next big move.
By combining an understanding of these key elements with sound risk management and technical analysis, traders can develop a nuanced approach to market entry and exit, position sizing, and trend identification.
