In this session, we delve into the intricate concepts of inside price action and institutional market structure, crucial elements for understanding the dynamics of the Forex market.
The focus here is on the significance of analyzing assets that are correlated and inversely correlated, offering a deeper insight into the movements and strategies of major market players. This analysis is key to grasping the underlying forces that drive the Forex market, providing traders with a more comprehensive understanding of how different currencies interact and influence each other.
Understanding Institutional Market Structure
In the realm of Forex trading, understanding institutional market structure is pivotal. This section explains the concept of analyzing major market players by examining assets that are correlated and inversely correlated. A key tool in this analysis is the US Dollar Index, which serves as a benchmark for the US dollar’s value against a basket of foreign currencies.
By observing the movements of the Dollar Index, traders can gain insights into the behavior of institutional market players. The discussion here focuses on how fluctuations in the Dollar Index correlate with movements in foreign currency pairs, offering valuable clues about potential market directions and strategies used by large financial institutions.
Correlation with Dollar index
The correlation between the Dollar Index and foreign currencies is a crucial aspect in Forex trading. This section delves into the impact of the Dollar Index’s movement on foreign currencies. The Dollar Index, which measures the value of the US dollar against a basket of major currencies, acts as a significant indicator for currency traders.
The concept of market symmetry is introduced here, highlighting how movements in the Dollar Index can reflect inversely in foreign currency pairs. For instance, a rising Dollar Index often signals a decline in foreign currencies and vice versa. This relationship is key to understanding market dynamics and can be instrumental in making informed trading decisions.
SMT (Smart Money Technique) Divergence
The concept of SMT (Smart Money Technique) Divergence plays a pivotal role in Forex trading. This section introduces SMT Divergence and its application in analyzing market conditions. The essence of SMT Divergence lies in observing the relationship between the Dollar Index and foreign currencies, particularly focusing on whether their movements are symmetrical (moving in opposite directions as expected) or non-symmetrical (not following the expected inverse relationship).
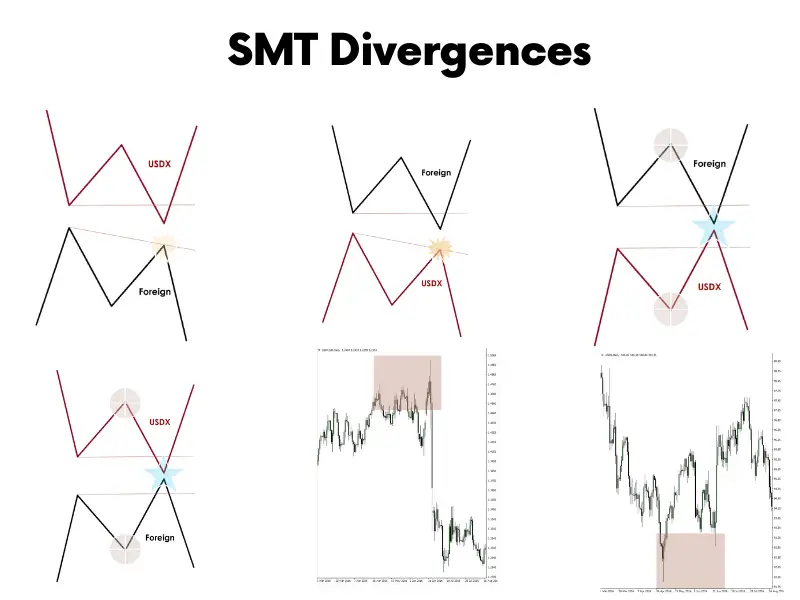
Symmetrical Market Conditions with Low USDX
- US Dollar Index Movement: When the US Dollar Index (USDX) makes a lower low than before.
- Foreign Currency Response: Correspondingly, a foreign currency typically reaches a higher high.
- Market Trend Confirmation: This pattern indicates that the existing market trend is likely to continue.
- Reversal Probability: Attempting to find reversal patterns in this scenario is not recommended due to low probability of success.
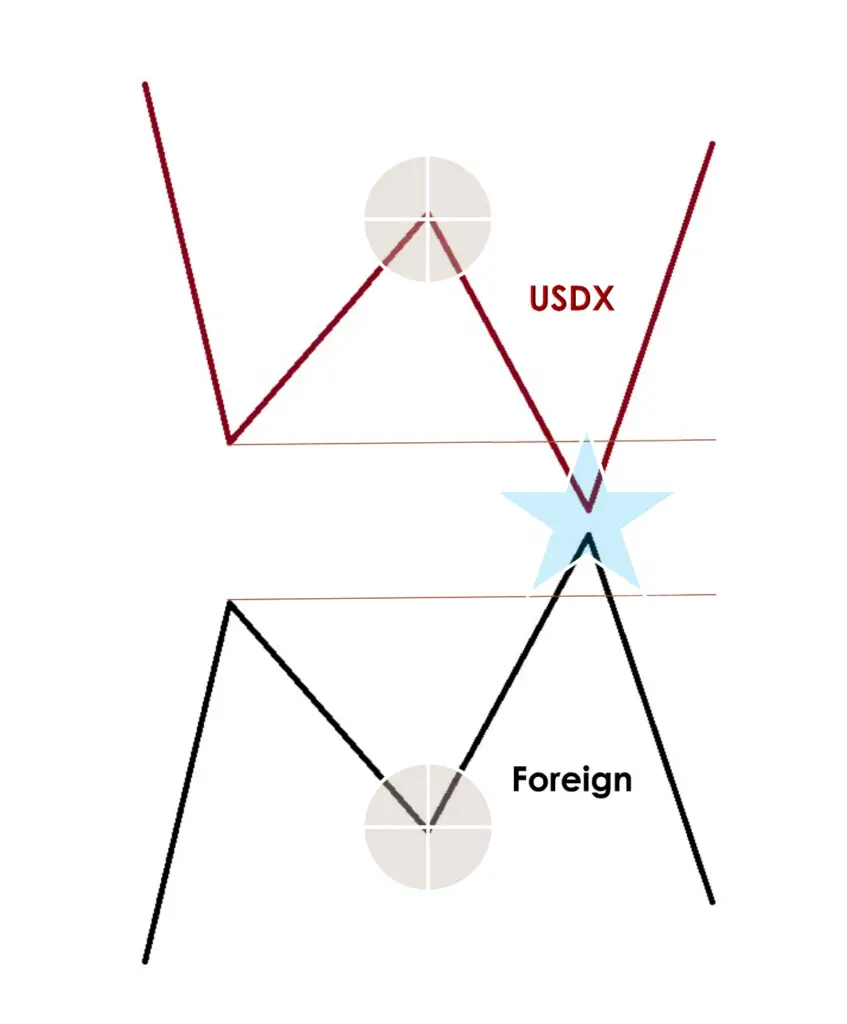
Symmetrical Market Conditions with High USDX
- US Dollar Index Movement: The US Dollar Index (USDX) records a higher high than its previous level.
- Foreign Currency Reaction: In contrast, a foreign currency will typically show a lower low.
- Confirmation of Market Trend: This occurrence confirms the ongoing market trend and suggests its likely continuation.
- Reversal Pattern Strategy: Seeking reversal patterns under these market conditions is generally low in probability and is not advised.
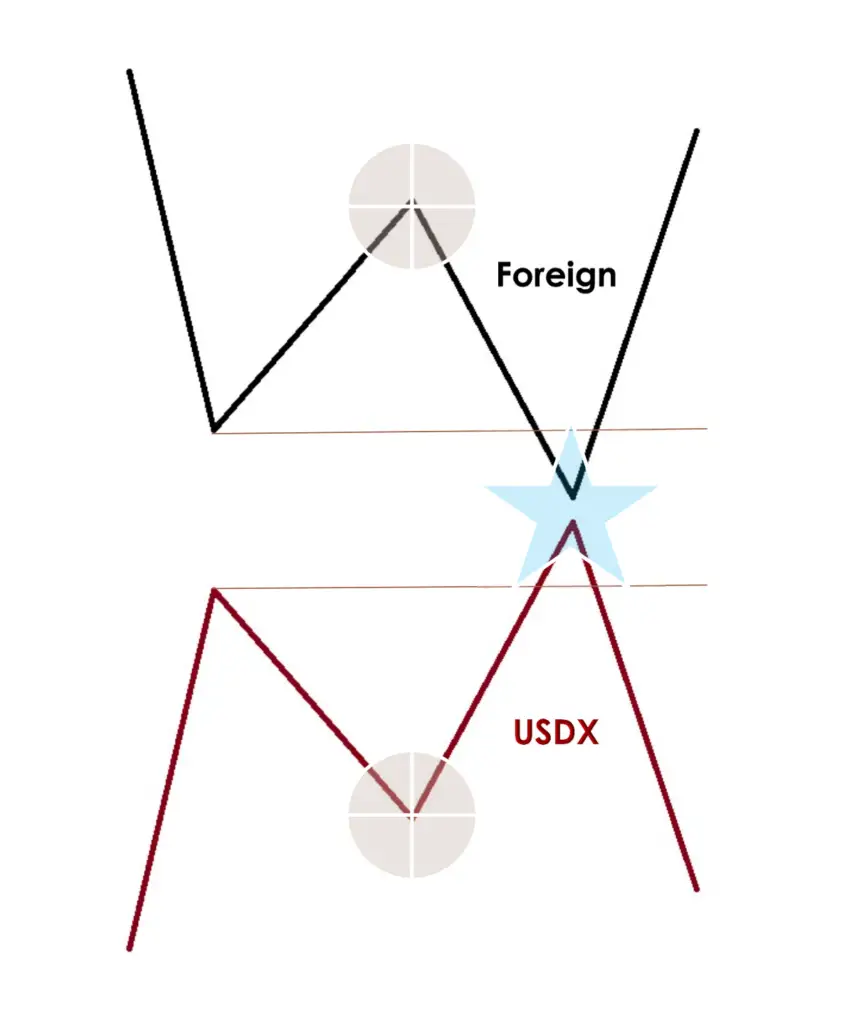
Non-Symmetrical Market Conditions with Low USDX
- US Dollar Index Movement: The US Dollar Index (USDX) experiences a lower low.
- Foreign Currency Reaction: Contrary to expectations, the foreign currency does not surpass its previous high – this is identified as a USDX SMT (Smart Money Technique) divergence.
- Lack of Trend Confirmation: This scenario fails to confirm the current price action, indicating that the underlying market trend may not continue.
- Reversal Pattern Strategy: Pursuing reversal patterns in this market condition is considered high probability and could be a reasonable trading approach.

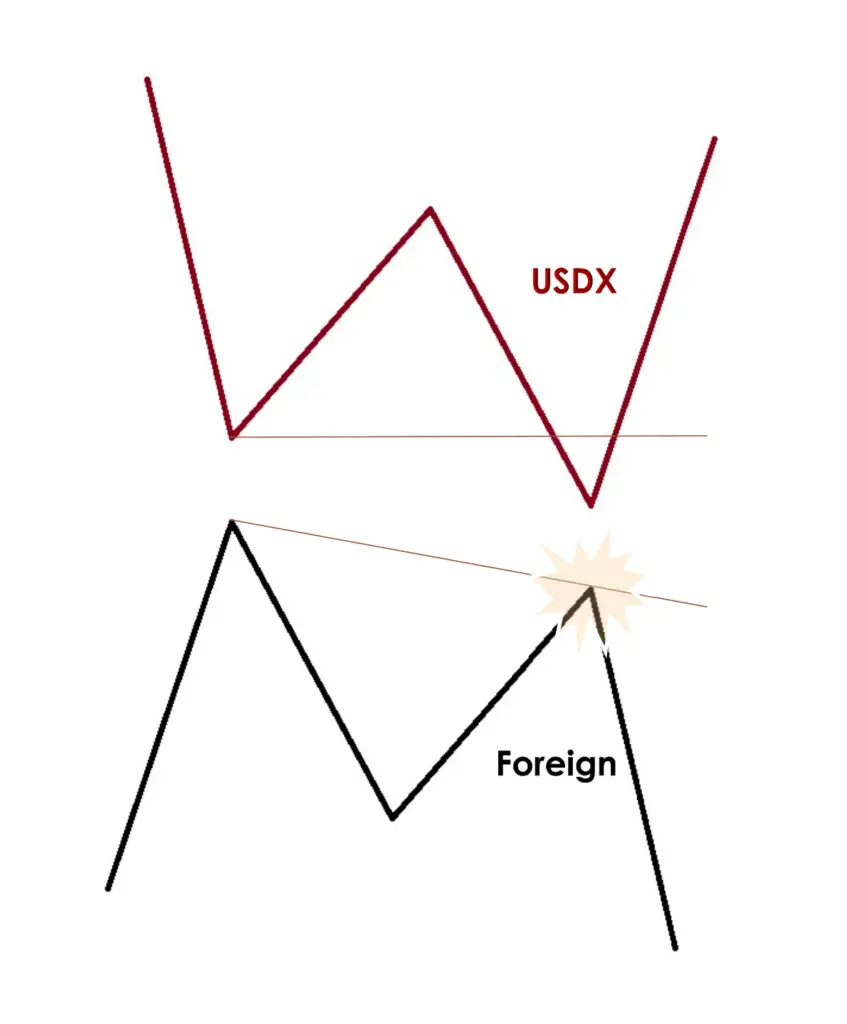
Non-Symmetrical Market Conditions with High USDX
- US Dollar Index Movement: The US Dollar Index (USDX) does not achieve a higher high.
- Foreign Currency Reaction: The foreign currency, in contrast, registers a lower low.
- Lack of Trend Confirmation: This pattern does not confirm the prevailing price action, suggesting that the ongoing market trend might not persist.
- Reversal Pattern Strategy: In these circumstances, looking for reversal patterns becomes a high-probability strategy and can be considered a reasonable approach.
Key points include:
- Analysis of Symmetrical Market Conditions: In symmetrical scenarios, a rise or fall in the Dollar Index is mirrored inversely by foreign currencies. For example, when the Dollar Index rises, foreign currencies typically fall, and vice versa. This symmetry confirms the current market trend and suggests its likely continuation.
- Analysis of Non-Symmetrical Market Conditions: Non-symmetrical conditions occur when the Dollar Index and foreign currencies do not move as expected. For instance, if the Dollar Index falls but a foreign currency does not rise correspondingly, this could indicate active intervention by smart money or large institutional players.
- Examples and Practical Application: The concept is further elucidated with practical examples. These examples demonstrate how traders can interpret divergences between the Dollar Index and foreign currencies to make informed trading decisions. This includes understanding when a non-symmetrical movement might signal a high probability of a trend reversal or continuation.
Case Studies: British Pound vs. USD (Cable) Using SMT Divergence
This section provides an in-depth analysis of real-world market scenarios, specifically focusing on the British Pound versus the United States Dollar (Cable), through the lens of Smart Money Technique (SMT) Divergence. It involves identifying and understanding potential divergence points between the Cable and the US Dollar Index, which offer valuable insights into market trends and trader behavior. The key aspects of this analysis include:
- Identifying Divergence Points: The study involves pinpointing specific instances where the Cable and the US Dollar Index do not move in their typically expected inverse relationship. These divergence points are crucial as they can signal a potential shift in market trends or highlight institutional market manipulation.
- Interpreting Market Signals: Each divergence point is analyzed to understand what it signals in the market. For example, if the Cable makes a higher high while the Dollar Index fails to make a corresponding lower low, it could indicate underlying strength in the Dollar, suggesting a potential bullish trend for the Dollar or a bearish trend for the Cable.
- Real-World Examples: The concept is further elucidated through real-world examples. These examples showcase how traders can use SMT divergence in practical scenarios to make informed trading decisions. The case studies are designed to provide a clear illustration of how divergence analysis can be applied to real market data, enhancing the trader’s ability to forecast and react to market movements effectively.
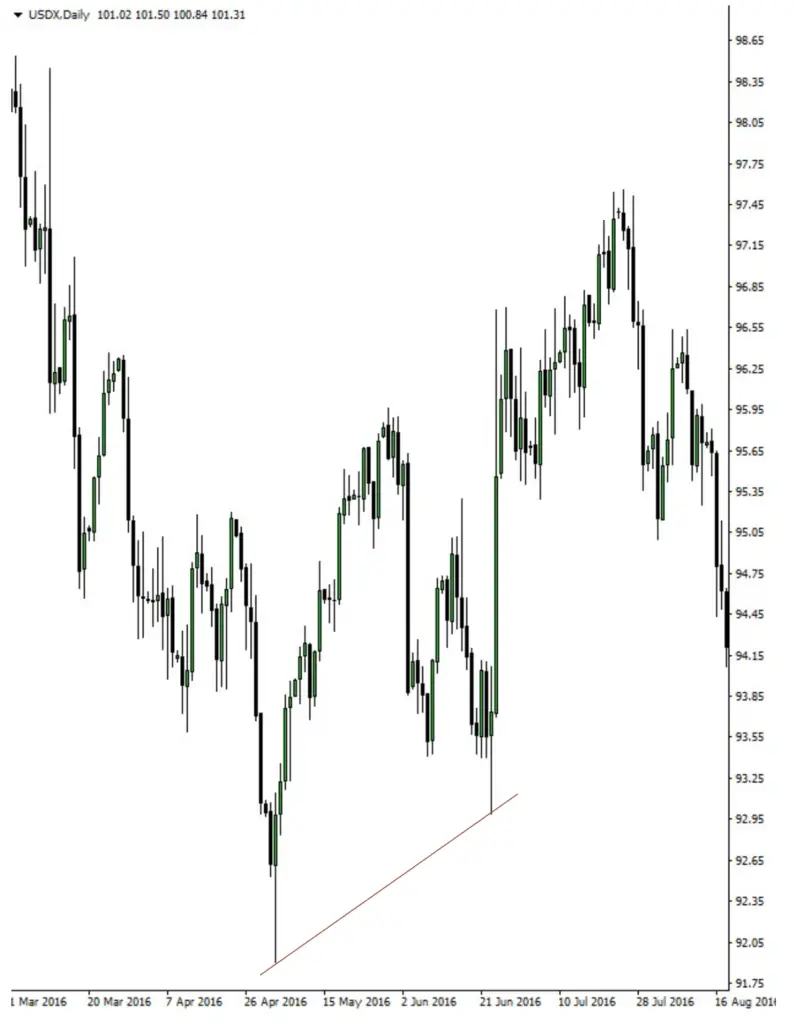
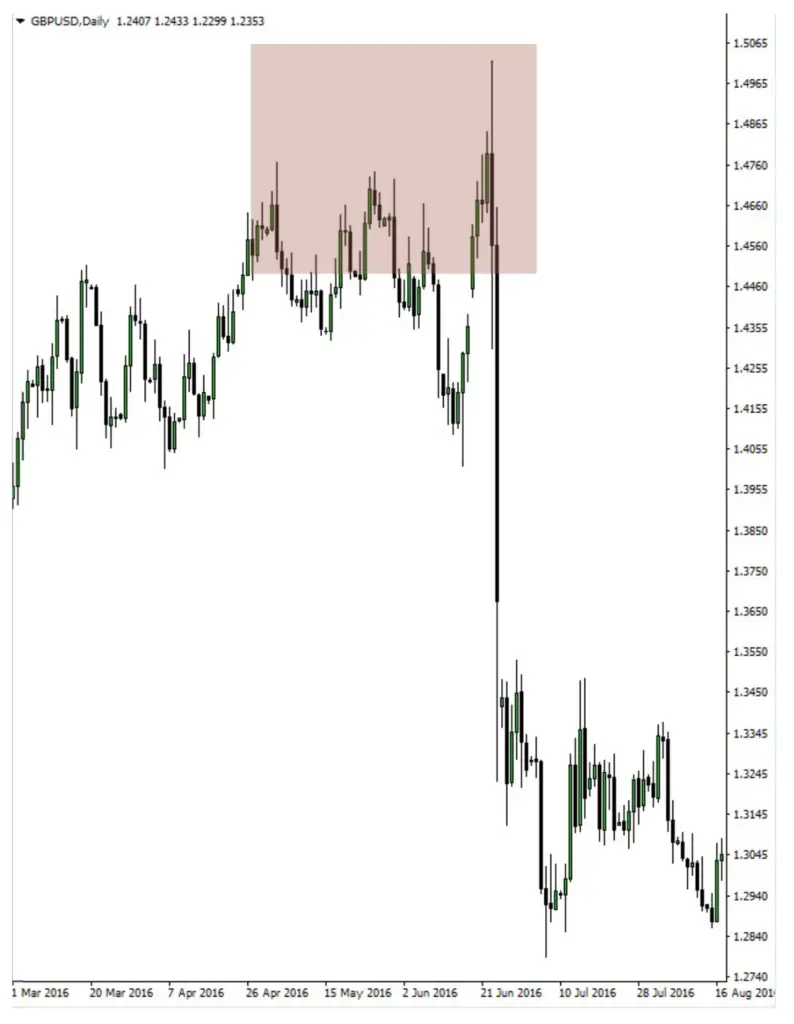
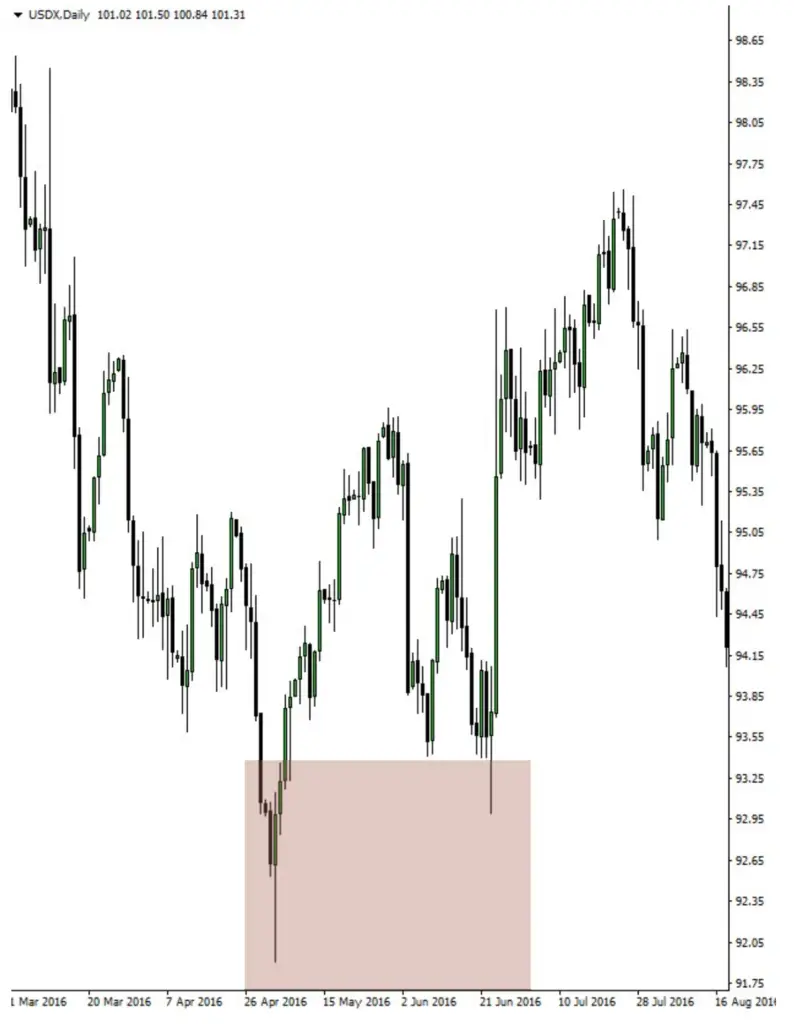
By studying these case studies, traders can gain a better understanding of how to apply SMT divergence in their analysis.
Conclusion
This article showed us how to read the Forex market by looking at big players and their impact. We learned that watching the US Dollar Index can give us clues about what might happen with other currencies. It’s like figuring out a puzzle – if the Dollar Index goes one way, certain foreign currencies often go the other way.
We also talked about SMT Divergence, a fancy term for spotting when the usual patterns don’t happen. This is like a secret signal that something interesting might be about to happen in the market.
The real-world examples, especially with the British Pound vs. the USD, were super helpful. They showed us how to use all this theory in actual trading. By looking at these examples, we can start to spot when the big market players are making moves, and use that to make smarter trading decisions.
In short, the big takeaway is that by understanding how the big players move and how different currencies are linked, we can make better guesses about where the market’s headed. This can be a real game-changer in our trading strategies.