In ICT (Inner Circle Trader) trading, two critical concepts are impulse price swings and market protraction. Both play significant roles in understanding market movements and timing trades effectively.
Impulse Price Swings
An impulse price swing is characterized by rapid and substantial market movements. These can manifest as a series of alternating movements: a sharp decline followed by a rapid ascent, and then another swift decline. This sequence results in creating distinct patterns of market highs and lows.
The Structure of Impulse Price Swings
| Swing Type | Market Behavior | ICT Trading Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Downward Swing | Rapid price decrease | Indicates potential bearish momentum |
| Upward Swing | Swift price increase | Suggests a shift to bullish momentum |
| Subsequent Swings | Alternating quick rises and falls | Forms a pattern that helps in identifying market trends |
Significance for Traders
- Market Momentum: These swings are indicative of the market’s momentum. By analyzing the direction and strength of impulse swings, traders can gauge the prevailing market sentiment.
- Turnaround Points: They often signal potential turning points in the market. For instance, a sharp upward swing following a downward move might indicate a reversal of trend.
- Predicting Market Direction: In ICT trading, recognizing these patterns is crucial for forecasting where the market is likely to move next.
Market Protraction
Market protraction is closely related to impulse price swings but has a unique element of time sensitivity. It refers to a price swing that is particularly influenced by the time of day. There are typically three main protractionary market moves in a 24-hour cycle:
- At 0 GMT: A movement up or down right at this time can indicate the start of a significant market shift.
- London Session: After midnight New York time, the market might make a move that could be deceptive, intended to mislead traders about the actual market direction.
- New York Session: At 7 AM New York time, the market might make another move, which is generally counter to the market’s overall direction, serving as a manipulation tactic to draw traders to the wrong side of the market.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Impulse Swings | Market Protraction |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Can occur at any time | Time-bound, occurring at strategic moments |
| Purpose | Indicate market momentum and trend reversals | Designed to manipulate trader psychology and exploit liquidity |
| Occurrence | Random, based on market dynamics | Occurs during specific trading sessions or hours |
| Trader Response | Used to identify entry and exit points | Requires caution to avoid being misled by intentional market moves |
Significance in ICT Trading
- Impulse Swings: They provide a real-time view of the market’s direction and strength, helping traders to make timely decisions.
- Market Protraction: It serves as a reminder to be wary of deceptive market moves, especially during key market hours known for manipulation tactics.
Conclusion
To wrap up, understanding impulse price swings and market protraction is key in ICT (Inner Circle Trader) trading. Impulse swings help you see where the market is going fast, without worrying about the time. Market protraction is about knowing when during the day these moves might be tricks to watch out for.
For ICT traders, it’s all about using both these ideas to make smart choices. This means knowing when to jump in or out of trades, and not getting fooled by moves that look real but aren’t. In short, good ICT trading is about seeing the whole picture – both what the market is doing and when it’s doing it.

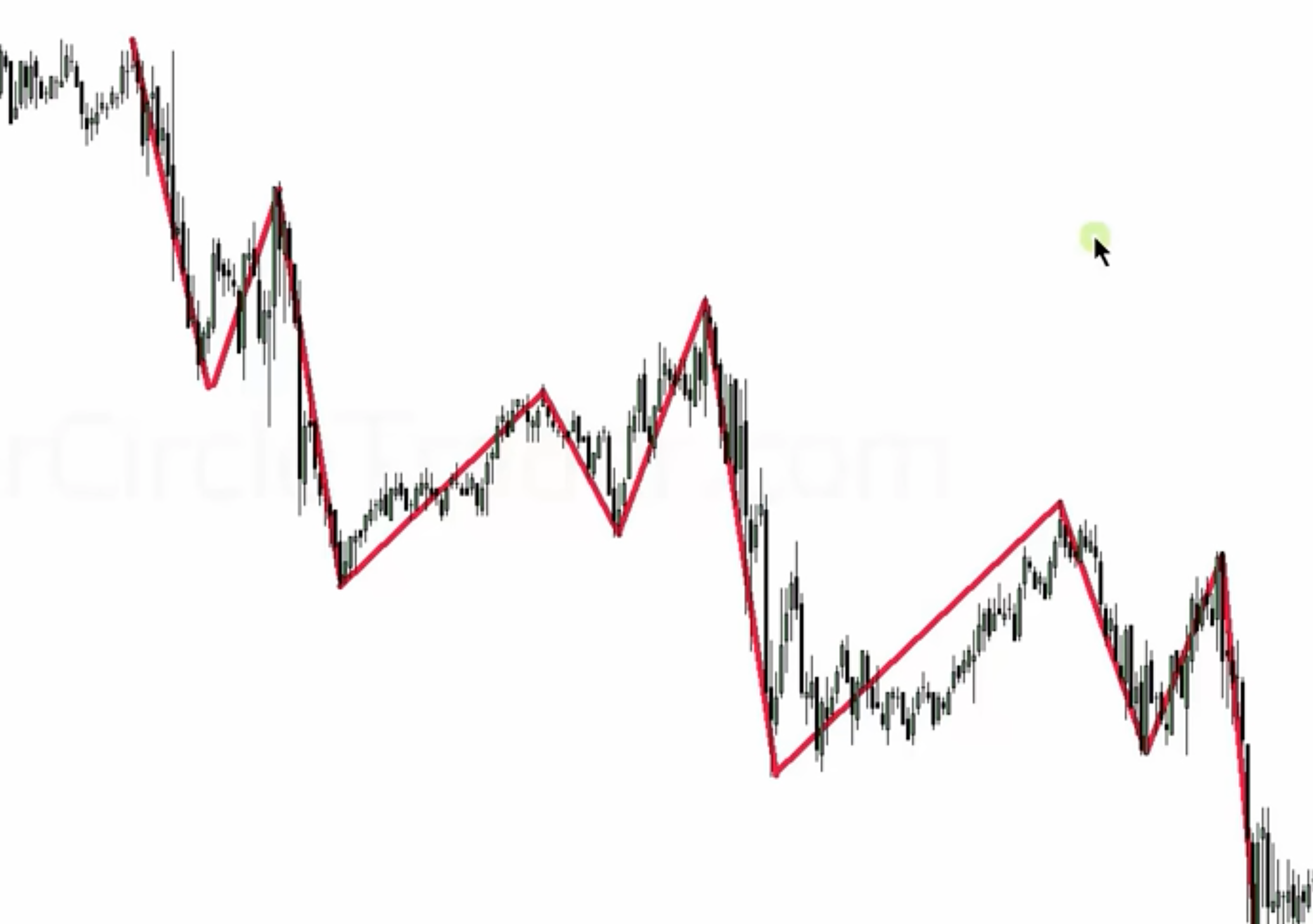
What time zone’s on london time are these?