Welcome to the fourth session of the ICT Mentorship. Today, we’re exploring ‘Equilibrium vs. Discount’ in trading, a crucial concept for both beginners and seasoned traders.
table summarizing the key concepts:
| Concept | Description | Application in Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Impulsive Price Swings | Recognize and analyze significant upward movements in the market. | Chart and monitor impulsive price swings on daily charts. |
| Equilibrium Point | Understand the midway point of a price move as the market’s fair value. | Observe market behavior as it approaches and enters the equilibrium zone. |
| Discount Market Conditions | Identify opportunities for buying when the market trades below the equilibrium. | Look for potential trade setups when the market is in a discount phase. |
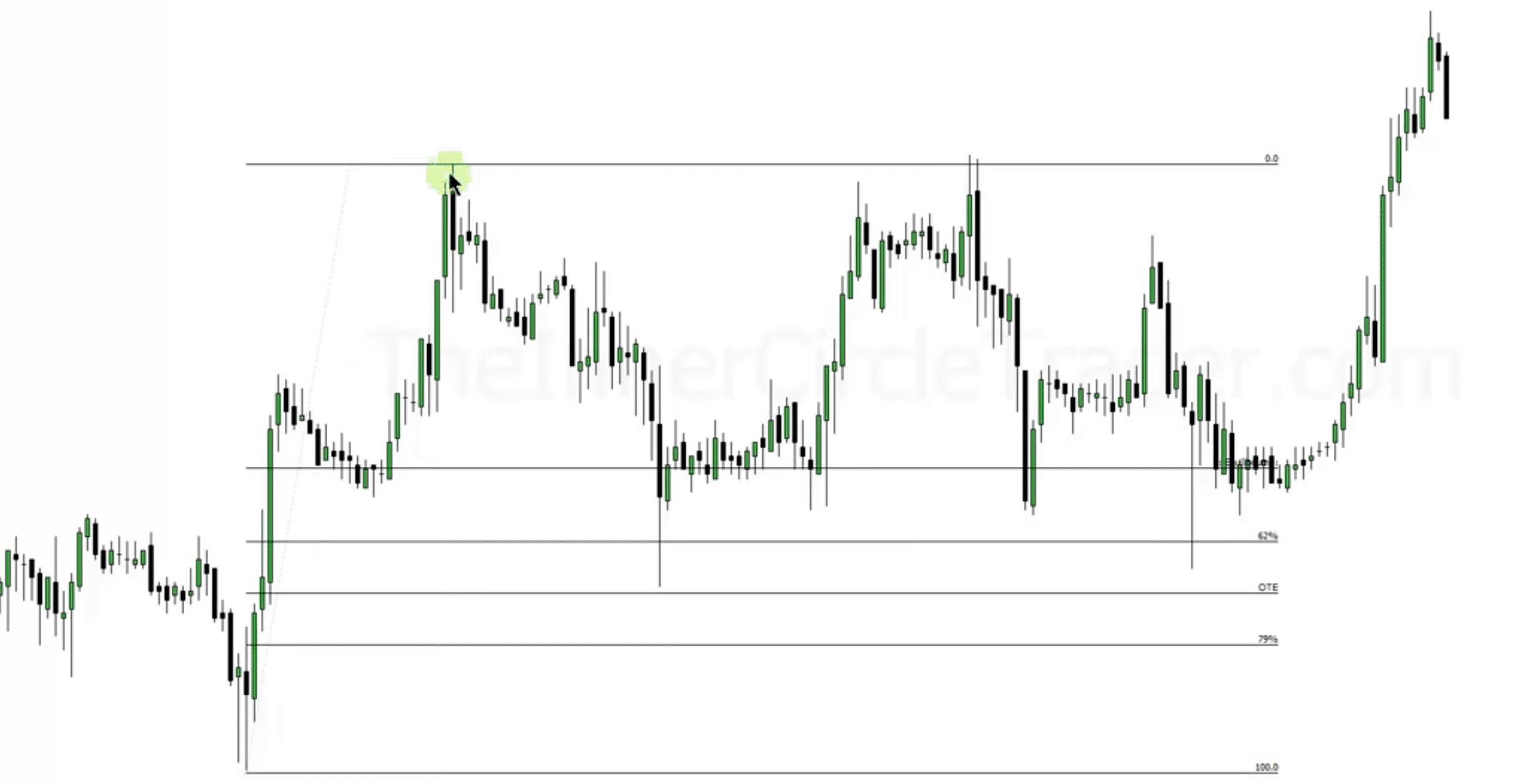
Understanding Market Equilibrium
Equilibrium in the market is the halfway point of a price movement. It’s essential for:
- Framing Market Conditions: Helps in assessing if the market price is fair or not.
- Reference Point: Acts as a benchmark for determining the market’s state – whether it’s at a fair value or stretched too far in one direction.
Optimal Trade Entry Using Fibonacci
We revisit the concept of Optimal Trade Entry, which involves:
- Using Fibonacci Tools: Identifying points in the market where a reversal or continuation might happen.
- No Magic in Fibonacci: It’s crucial to understand that Fibonacci levels are just guides, not guaranteed turning points.
Key Points for Traders
- Identify Swing Highs and Lows: Look for major movements in the market and use Fibonacci to find potential reversal points.
- Equilibrium as a Starting Point: Use the midpoint of a big price swing as your starting reference for assessing market conditions.
- Discount Market Opportunities: When the market is trading below this midpoint, it might present buying opportunities, as it’s considered ‘discounted’.
Analyzing Price Swings
- Swing High Formation: Watch for a significant upward movement in the market, known as a swing high.
- Observe Market Retracement: After a swing high, monitor how the market retraces back towards the equilibrium point.
Practical Application in Trading
- Map Price Swings: Regularly chart impulsive price swings on daily charts to understand market movements.
- Monitor Equilibrium Approach: Observe how the market behaves as it nears and enters the equilibrium zone.
- Identify Trade Conditions: Look for signs that the market is in a discount phase for potential trade setups.
Conclusion
This mentorship session provides essential insights into understanding equilibrium and discount in the market. Grasping these concepts is vital for developing trading strategies that resonate with the market’s natural rhythm and the behavior of institutional players. By focusing on these principles, traders can improve their skills in spotting high-probability trading opportunities.